【SUMMARY】
Acute diarrheal disease in young children is a major cause of
morbidity worldwide and is a leading cause of mortality in developing
countries. 1 Research has shown that enteric adenoviruses, primarily Ad40 and
Ad41, are a leading cause of diarrhea in many of these children, second only to
the rotaviruses. These viral pathogens have been isolated throughout the world,
and can cause diarrhea in children year round. Infections are most frequently
seen in children less than two years of age, but have been found in patients of
all ages. Further studies indicate that adenoviruses are associated with 4-15%
of all hospitalized cases of viral gastroenteritis. Rapid and accurate
diagnosis of gastroenteritis due to adenovirus is helpful in establishing the
etiology of gastroenteritis and related patient management. Other diagnostic
techniques such as electron microscopy (EM) and nucleic acid hybridization are
expensive and labor-intensive.
With the self-limiting nature of adenovirus infection, such expensive and
labor-intensive tests may not be necessary.
The Adenovirus Rapid Test Cassette (Feces) is a rapid chromatographic
immunoassay for the qualitative detection of adenovirus in human feces
specimen, providing results in 10 minutes. The test utilizes antibody specific
for adenovirus to selectively detect adenovirus from human feces specimens.
【DIRECTIONS
FOR USE】
Allow the test, specimen, buffer, and/or controls to reach room temperature
(15-30°C)
prior to testing.
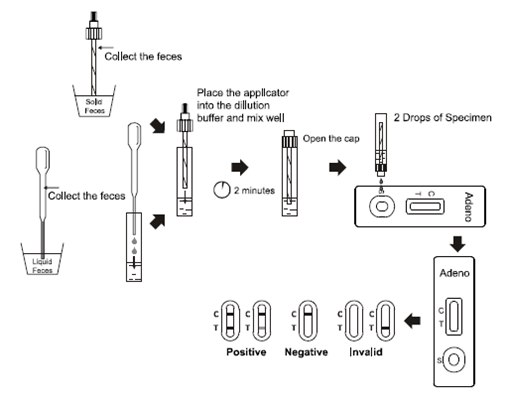
1. To collect fecal specimens:
Collect sufficient quantity of feces (1-2mL or 1-2g) in a clean, dry specimen
collection container to obtain enough virus particles. Best results will be
obtained if the assay is performed within 6 hours after collection. Specimen
collected may be stored for 3 days at 2-8°C if not tested within 6 hours. For
long term storage, specimens should be kept below -20°C.
2. To process fecal specimens:
For Solid Specimens:
Unscrew the cap of the specimen collection tube, then randomly stab the
specimen collection applicator into the fecal specimen in at least 3 different
sites to collect approximately 50 mg of feces (equivalent to 1/4 of a pea). Do
not scoop the fecal specimen.
For Liquid Specimens:
Hold the dropper vertically, aspirate fecal specimens, and then transfer 2
drops of the liquid specimen (approximately 50 µL) into the specimen collection
tube containing the extraction buffer.
Tighten the cap onto the specimen collection tube, then shake the specimen
collection tube vigorously to mix the specimen and the extraction buffer. Leave
the collection tube for reaction for 2 minutes.
3. Bring the pouch to room temperature before opening it. Remove the test
cassette from the foil pouch and use it as soon as possible. Best results will
be obtained if the test is performed immediately after opening the foil pouch.
4. Hold the specimen collection tube upright and unscrew the tip of the
specimen collection tube. Invert the specimen collection tube and transfer 2
full drops of the extracted specimen (approximately 80 mL) to the specimen well
(S) of the test cassette, then start the timer. Avoid trapping air bubbles in
the specimen well (S). See illustration below.
5. Read the results at 10 minutes after dispensing the specimen. Do not read
results after 20 minutes.
Note: If the specimen does not migrate (presence of particles), centrifuge the
diluted sample contained in the extraction buffer vial. Collect 80 µL of
supernatant, dispense into the specimen well (S). Start the timer and continue
from step 5 onwards in the above instructions for use.